數據科學研究中心下的研究項目是高度跨學科的,涉及澳門大學所有學系。
跨境數據流動的制度建設與第三方平臺設計
本項目旨在為GMCZ跨境數據傳輸提供切實可行的解決方案。具體來說,我們將首先檢視在GDPR框架下,澳門與中國內地在個人資料保護問題上的法律制度差異,並嘗試為跨境數據傳輸定義一個既能確保資料安全又能促進數位經濟創新的共同法律基礎。
網上用戶互動-基於數據的跨領域研究
本項目的研究重點是利用網路數據瞭解不同人口特徵的個體與組織在不同環境中的互動。具體而言,其目標是基於從互聯網上獲取的使用者行為數據,建立一個關於網絡用戶交互機制和效果的理論框架,並在此框架的基礎上解決社會科學不同領域的實際問題。預計將予以填補社會科學領域的相關研究空白,即以更便捷的方式獲取關於互動的數據,並明確參與互動的過程中各方角力所發揮的重要作用。
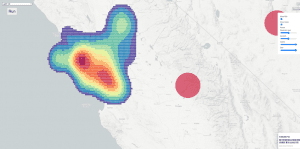
COVID-19 熱圖視覺化系統
- http://degroup.cis.um.edu.mo/covid-19/
- 在這個與香港大學的聯合計畫中,我們的團隊建立了一個視覺化系統來展示最先進的熱圖視覺化演算法。
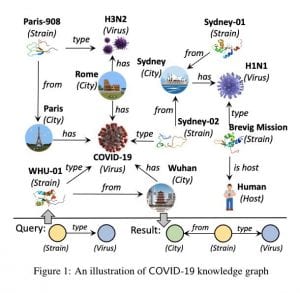
COVID-19 知識圖模式發現
- 在這個與南方科技大學的聯合計畫中,我們的團隊研究了大型知識圖中最先進的模式發現演算法。
- 我們系統的查詢引擎在回應時間方面優於最先進的解決方案 10~100 倍。