(LibKDV, https://github.com/libkdv/libkdv).
One important lesson from this pandemic is that, given the rapid spread of the virus, it is increasingly necessary to use information technology to expedite epidemic prevention and control, acting swiftly to counteract the spread. It is recommended to draw on the experiences of relevant regions that have applied information technology and, in conjunction with local circumstances, to innovate and develop new applications for epidemic prevention information technology, such as location-based epidemic warning notifications.
By building a digital epidemic prevention system, we can provide the public with channels to obtain and actively report epidemic information while protecting personal information, thereby reducing the government’s cost of epidemic information and improving response efficiency.
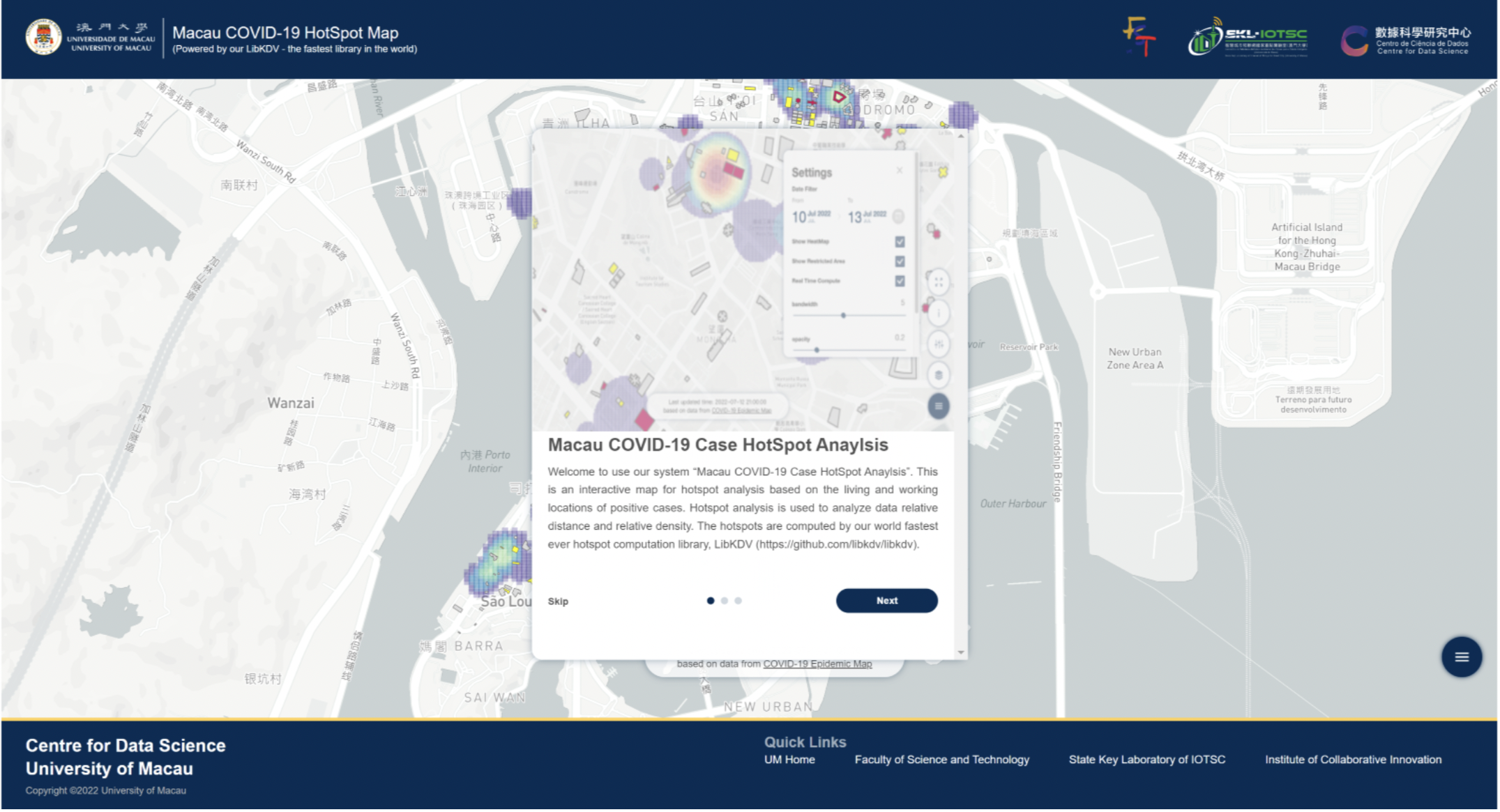
The University of Macau has established a “COVID-19 Hotspot Analysis System,” which allows the public to log in to the system at:degroup.cis.um.edu.mo/covid-19/to get the changes in the epidemic。
Citizens can select dates from the system’s menu and use the map function to choose location ranges for hotspot analysis calculations. The red areas indicate regions with a relatively high number of positive cases, which can serve as a reference for personal risk assessment when going out. The system provides information on positive cases and lockdown situations for various buildings from the Macau Health Bureau’s COVID-19 epidemic map, while the core algorithms for hotspot calculation are supported by the hotspot calculation technology developed by the University of Macau’s National Key Laboratory for Smart City Internet of Things (LibKDV, https://github.com/libkdv/libkdv) 。
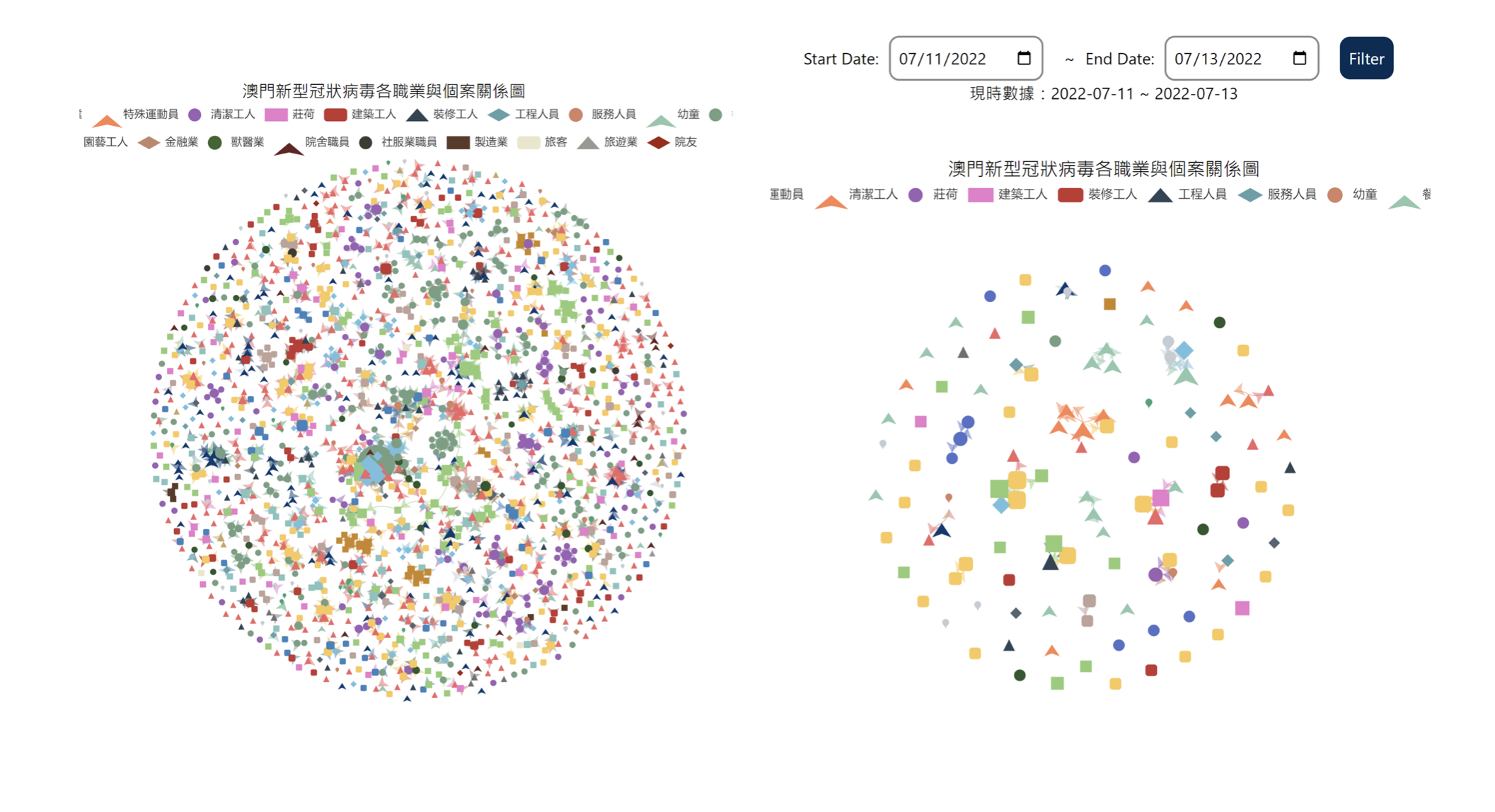
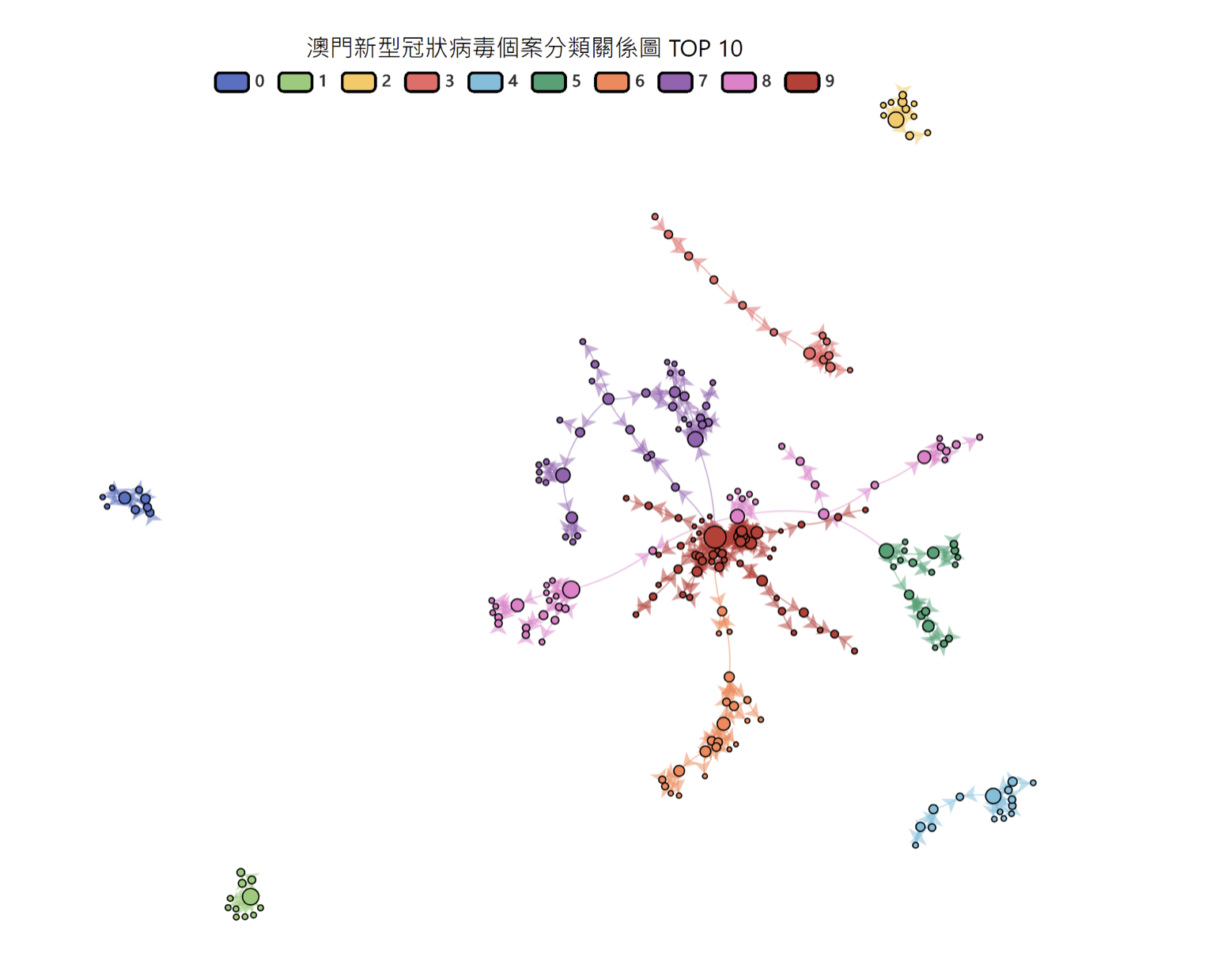
The research team is also analyzing COVID-19 data and developing various composite data processing systems for research use, including data cleaning, geographic information conversion, data querying, data presentation, and data analysis. For example, Figure 2 shows the relationship diagram of positive cases, used to analyze the case situation of different professions and regions at various time periods; Figure 3 uses Markov Chain and graph segmentation techniques to assist other research units in finding relationships among positive cases and key populations.